Content briefs should be strategic documents that guide writers toward creating high-performing content. Instead, they're often generic templates with minimal guidance—if they exist at all.
The result? Content that misses search intent, ignores competitive positioning, and requires extensive revisions. Your team wastes hours creating briefs manually, and writers still don't have what they need to succeed.
Custom GPTs solve this problem by encoding your specific content strategy into an AI tool that generates comprehensive briefs in minutes. Not generic templates—briefs tailored to your industry, audience, and SEO methodology.
This guide walks through building a custom GPT for content brief generation, with specific configurations, prompt engineering strategies, and quality control processes that work at scale.
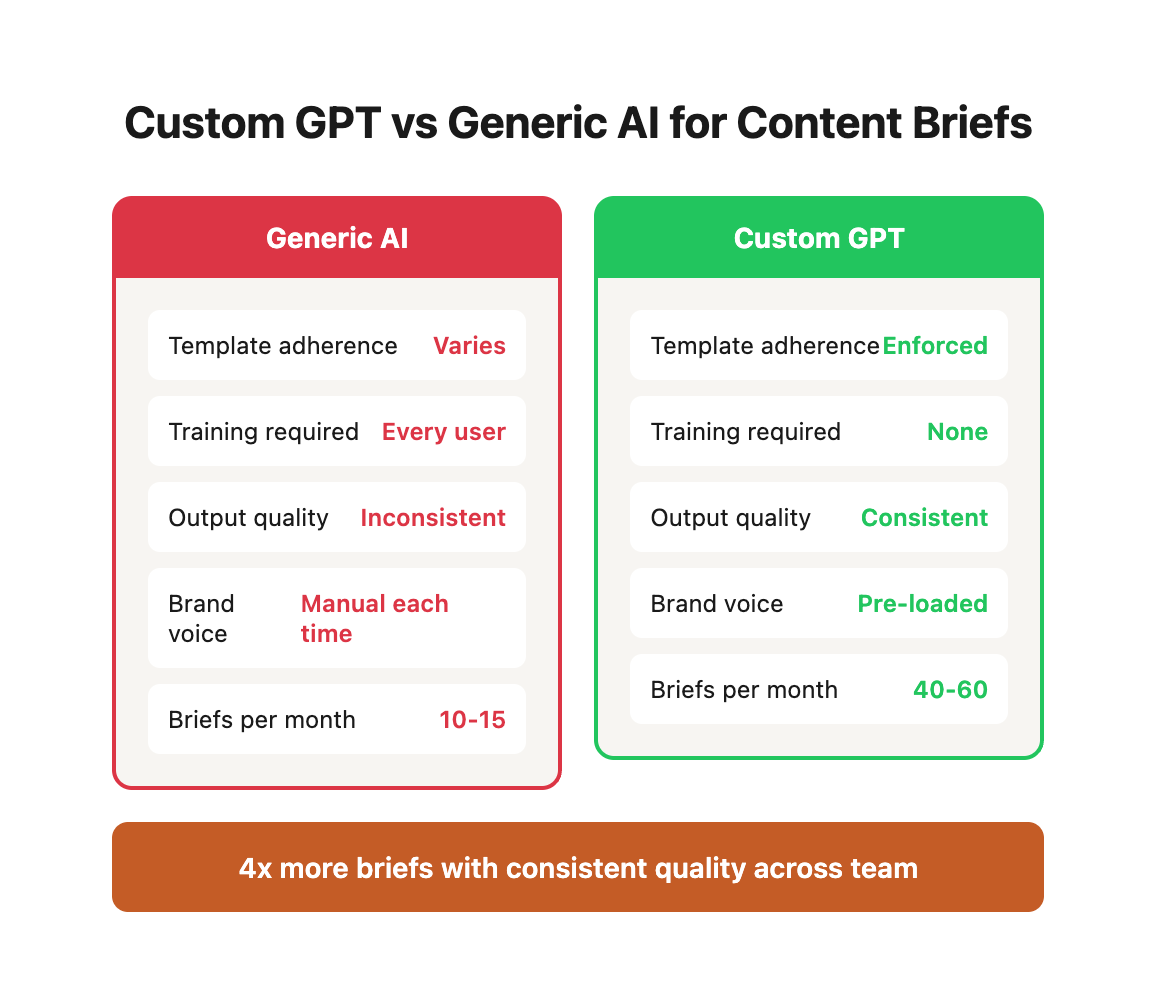
Why Custom GPTs Beat Generic AI for Content Briefs
Standard ChatGPT or Claude can generate content briefs. So why build a custom GPT?
The Consistency Problem with Generic AI
When you use vanilla ChatGPT for content briefs, you're starting from zero with every request. Each team member writes their own prompt. One person asks for "an SEO brief for best CRM software," another requests "a content outline for CRM comparison article," and a third wants "keyword research for CRM tools."
The result? Three completely different brief formats with inconsistent quality. Your writers receive varying levels of guidance, SEO requirements get missed, and your content program lacks the systematic approach that drives repeatable results.
Custom GPTs solve this through encoded consistency:
Domain-specific knowledge baked in:
Generic AI knows about content marketing broadly. Your custom GPT knows that your SaaS customers are mid-market operations directors who care about implementation time more than feature count. It knows your target audience reads at a 10th-grade level. It knows you never use terms like "revolutionary" or "game-changing" because that's not your voice.
This context shapes every recommendation. When analyzing competitors, your GPT evaluates them through your positioning lens. When suggesting headings, it targets the specific keyword variations your audience actually uses. When recommending word count, it factors in what has historically performed for your domain authority and content type.
Workflow integration that drives velocity:
Team accessibility transforms scalability:
Before custom GPTs, only your SEO lead could create high-quality briefs. This created a bottleneck where content production was limited by one person's bandwidth. Now your entire content team—writers, editors, project managers—can generate briefs that meet your standards.
This isn't about removing expertise from the process. Your SEO specialist still reviews and refines. But their time shifts from manual brief creation to strategic oversight and optimization. Instead of spending 20 hours per week writing briefs, they spend 5 hours reviewing AI-generated briefs and 15 hours on higher-leverage activities like technical SEO or strategy development.
Real-World Performance Comparison
We implemented custom GPT-based briefing for three clients with different content volumes:
Think of a custom GPT as your content strategist who never sleeps, never forgets your guidelines, and produces consistent output regardless of workload. But unlike a human strategist, it costs $20/month and scales infinitely.
The Anatomy of an Effective SEO Content Brief
Before building your custom GPT, define what makes a brief valuable to your team.
A content brief serves three masters: search engines (ranking signals), writers (clear direction), and readers (valuable information). Most briefs over-optimize for one at the expense of the others. SEO-heavy briefs become keyword-stuffing checklists. Writer-focused briefs lack strategic direction. Reader-centric briefs ignore search visibility.
The framework below balances all three by structuring information in layers: strategic context → technical requirements → creative guidance → quality standards.
The Five-Layer Brief Framework
Here's our proven brief structure that balances SEO requirements with creative freedom:
Section 1: Strategic Context
This layer answers "why are we creating this content?"
- Primary keyword and search intent: Not just the keyword phrase—what problem is the searcher trying to solve? Are they learning, comparing, or ready to buy?
- Target audience segment: Demographics matter less than psychographics. What's their current knowledge level? What objections do they have? What alternative solutions have they already tried?
- Content goal: Map to funnel stage explicitly. Top-of-funnel awareness content has different success metrics than bottom-of-funnel conversion content.
- Competitive positioning: How will this content be demonstrably different from the top 5 results? "Better" isn't a strategy—specific differentiation is.
Example strategic context:
Primary Keyword: "how to reduce cart abandonment"
Search Intent: E-commerce managers looking for tactical strategies to implement immediately
Audience Segment: Mid-market retailers (10-100 employees), Shopify/WooCommerce users,
frustrated with 70%+ abandonment rates, limited development resources
Content Goal: Lead generation (email capture via downloadable audit checklist)
Positioning: Unlike competitor content focused on broad strategies, we provide
platform-specific implementation steps with before/after examples
Section 2: SEO Requirements
Technical elements that satisfy search algorithms.
- Title tag (50-60 characters): Primary keyword + emotional hook or benefit. Test multiple options with different angle emphasis.
- Meta description (150-160 characters): Not a ranking factor but directly impacts CTR. Include primary keyword, specific benefit, and action prompt.
- URL slug: Match primary keyword. Avoid stop words. Keep under 60 characters. Use hyphens, not underscores.
- Primary keyword: Exact match phrase. Document search volume, difficulty, and current ranking position if applicable.
- Secondary keywords (5-10): Related terms with independent search volume. Include question variations and synonyms.
- Keyword placement guidance: Specific location instructions prevent both keyword stuffing and under-optimization.
Keyword placement framework:
Section 3: Content Structure
The architectural blueprint for the piece.
- Recommended H2 headings (6-10): Each targets a keyword variation or answers a question from PAA/forums. Include the target term in brackets after each heading suggestion.
- Word count target: Not arbitrary. Based on median length of top 5 results +20% for comprehensiveness advantage. Document your competitive analysis.
- Content depth indicators: Which sections need 500+ words with examples vs. which need 100 words of definition? This prevents scope creep and under-development.
- Internal linking opportunities: Specific URLs to reference, exact anchor text, and contextual placement suggestions. Minimum 3-5 internal links per post.
H2 structure example with keyword targeting:
1. What Causes Shopping Cart Abandonment? [cart abandonment causes]
2. 7 Proven Strategies to Reduce Cart Abandonment [reduce cart abandonment]
3. How to Optimize Your Checkout Process [checkout optimization]
4. Retargeting Tactics for Abandoned Carts [cart abandonment email]
5. Platform-Specific Solutions for Shopify Users [shopify cart abandonment]
6. Measuring and Improving Your Recovery Rate [cart abandonment rate]
Section 4: Research Foundation
Competitive intelligence that informs differentiation.
- Top 5 ranking competitors: Don't just list URLs. Analyze each: word count, structure, strengths, weaknesses, and specific gaps in their coverage.
- Content gaps to exploit: What questions do they not answer? What examples do they lack? What outdated information do they present? Your content wins by filling these voids.
- Questions to answer: From People Also Ask, Reddit threads, Quora, industry forums. These are the long-tail variations that drive engaged traffic.
- Visual content suggestions: Not generic "add images." Specific: "comparison table of 5 cart abandonment tools," "flowchart of checkout optimization process," "screenshot of abandoned cart email example."
Competitor analysis matrix:
Section 5: Quality Criteria
Standards the finished piece must meet.
- Key takeaways: 3-5 actionable insights readers should gain. If someone only reads these, they should still get value.
- CTA guidance: What specific action do we want readers to take? Match to content goal. Awareness content → email signup. Decision content → demo request.
- Brand voice requirements: Specific to your organization. Not just "professional" or "friendly"—exact phrases to use/avoid, tone examples, perspective (we/you/they).
- Readability target: Specific Flesch-Kincaid grade level (typically 8-10 for B2B, 6-8 for B2C). Average sentence length. Active voice percentage.
Quality checklist:
□ Primary keyword appears naturally 5-8 times (0.5-1% density)
□ Every H2 targets a specific keyword variation or question
□ At least 3 specific examples or case studies included
□ Minimum 3 internal links to related content
□ 2-3 external links to authoritative sources
□ At least 2 visual elements (images, charts, diagrams)
□ Readability score 60+ (Flesch Reading Ease)
□ CTA appears in introduction and conclusion
□ Meta title and description optimized
□ URL slug matches primary keyword
Why this structure works: It gives writers clear direction without micromanaging. SEO requirements are explicit, but creative execution remains flexible. Strategic context prevents writing in a vacuum. Research foundation eliminates guesswork. Quality criteria ensure consistency.
Your custom GPT's job is to populate every section with research-backed, specific guidance—not generic templates, but tailored recommendations based on actual SERP analysis and your specific content standards.
Building Your Custom GPT: Step-by-Step Configuration
Here's how to build this in ChatGPT (similar process applies to Claude Projects or other platforms).
Step 1: Initial GPT Configuration
Name: "[Your Brand] Content Brief Generator" Description:
"Generates comprehensive SEO content briefs for [your industry/niche] following [your brand]'s proven content methodology. Includes keyword research integration, SERP analysis, competitive intelligence, and strategic positioning."
Custom GPT Configuration (JSON Format):
{
"name": "[Your Brand] Content Brief Generator",
"description": "Generates comprehensive SEO content briefs following proven methodology",
"instructions": "See system prompt below",
"conversation_starters": [
"Generate a brief for [keyword]",
"Create briefs for my content calendar [upload CSV]",
"Analyze top-ranking content for [keyword]",
"Suggest content topics for [industry/topic]"
],
"capabilities": {
"web_browsing": true,
"dalle_image_generation": false,
"code_interpreter": true
},
"welcome_message": "I'll help you create comprehensive SEO content briefs. Upload your keyword list, provide a target keyword, or ask me to analyze competitor content."
}
Instructions (System Prompt):
```
You are an expert SEO content strategist for [Your Brand], specializing in [your industry/niche]. Your role is to generate comprehensive content briefs that guide writers to create high-performing content.
BRIEF STRUCTURE:
Use this exact structure for every brief you generate:
Strategic Context
- Primary Keyword & Search Intent
- Target Audience Segment
- Content Goal
- Competitive Positioning
SEO Requirements
- Title Tag (50-60 chars)
- Meta Description (150-160 chars)
- URL Slug
- Primary Keyword
- Secondary Keywords (5-10)
- Keyword Placement Guidance
Content Structure
- Recommended H2 Headings (6-10)
- Word Count Target
- Content Depth Indicators
- Internal Linking Opportunities
Research Foundation
- Top 5 Ranking Competitors (with analysis)
- Content Gaps to Exploit
- Questions to Answer (from PAA, forums)
- Visual Content Suggestions
Quality Criteria
- Key Takeaways (3-5 actionable insights)
- CTA Guidance
- Brand Voice Requirements
- Readability Target
BRAND VOICE GUIDELINES:
[Insert your specific voice and tone guidelines here. Example:]
- Direct and action-oriented, not vague or theoretical
- Data-backed assertions, specific numbers when available
- Partnership-oriented language ("we" not "you should")
- Professional but conversational tone
- No marketing jargon or empty superlatives
CONTENT STANDARDS:
- All briefs must be actionable and specific
- Every heading suggestion should target a keyword variation or question
- Competitor analysis must identify specific content gaps
- Word count targets should be 20% above median of top 5 results
- Internal linking suggestions must reference actual existing content
RESEARCH PROCESS:
When generating a brief:
1. Analyze search intent behind the primary keyword
2. Research top 10 SERP results for content patterns
3. Identify People Also Ask questions and related searches
4. Find content gaps competitors haven't addressed
5. Determine optimal content length and structure
6. Suggest specific angles that differentiate our content
VALIDATION CHECKLIST:
Before outputting a brief, verify:
- Primary keyword appears in title, meta, first H2
- Secondary keywords are naturally distributed across headings
- Word count target is competitive but achievable
- At least 3 specific content gaps identified
- All sections of the brief structure are complete
OUTPUT FORMAT:
Always format briefs in markdown for easy copying into content management systems.
```
Conversation Starters:
Add these buttons to make the GPT easy to use:
1. "Generate a brief for [keyword]"
2. "Create briefs for my content calendar [upload CSV]"
3. "Analyze top-ranking content for [keyword]"
4. "Suggest content topics for [industry/topic]"
Step 2: Knowledge Base Upload
Upload these documents to your custom GPT's knowledge base:
Essential files:
1. Your existing content inventory (CSV with URLs, titles, keywords, performance data)
2. Brand voice and tone guide (your specific writing guidelines)
3. Target audience research (personas, pain points, search behaviors)
4. Content performance benchmarks (average word count, engagement metrics by content type)
5. Internal linking strategy (priority pages for link building)
Optional but valuable:
1. Sample content briefs you've created manually that performed well
2. Competitor analysis documents
3. Keyword research exports from your SEO tool
4. Style guide and formatting requirements
Why knowledge base matters: The GPT references these documents when generating briefs, ensuring consistency with your existing strategy and accurate internal linking suggestions.
Step 3: Capabilities Configuration
Enable these features:
- Web Browsing: CRITICAL—allows real-time SERP analysis and competitor research
- DALL-E Image Generation: Optional—useful for suggesting visual content concepts
- Code Interpreter: Useful if you'll upload keyword research CSVs for batch processing
Disable:
- Third-party API access: Not needed for most content brief use cases
Step 4: Testing and Refinement
Generate 5-10 test briefs across different content types:
- Informational blog posts (top of funnel)
- Comparison/review content (middle of funnel)
- Product/service pages (bottom of funnel)
- Technical documentation
- FAQ pages
Evaluate each brief:
- Is keyword placement guidance specific and natural?
- Do heading suggestions target variations and questions?
- Are competitor gaps accurately identified?
- Would a writer have clear direction from this brief?
- Does it maintain your brand voice?
Refinement process:
When you find issues, update the system prompt. Example:
Issue: GPT suggests generic headings like "Introduction" or "Conclusion" Fix: Add to instructions:
"Never suggest generic headings like 'Introduction,' 'Overview,' or 'Conclusion.' Every H2 must target a specific keyword variation, answer a question, or address a user need."
Issue: Competitor analysis is superficial Fix: Add requirement:
"When analyzing competitors, identify at least 3 specific weaknesses in their content: missing information, poor examples, outdated data, confusing explanations, etc. Explain how our content will be superior in each area."
Iterate until briefs consistently meet your quality standards.
Advanced Prompt Engineering for Better Briefs
The system prompt is your foundation. These advanced techniques improve output quality.
Most custom GPT failures trace back to weak system prompts. Teams write vague instructions like "create high-quality SEO briefs" and wonder why outputs are inconsistent. The GPT has no definition of "high-quality" and no framework for "SEO."
Effective prompt engineering is about constraint and specificity. You're not giving the AI freedom to be creative—you're encoding your expertise into a reproducible process.
The Prompt Engineering Hierarchy
We're building toward Level 5. Here's how.
Technique 1: Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Add this to your system prompt:
```
Before generating the final brief, think through:
1. What is the searcher's actual goal? (not just what they typed)
2. What stage of awareness/buyer journey is this content for?
3. What misconceptions might searchers have that we need to address?
4. What format best serves this intent? (listicle, guide, comparison, etc.)
Show this reasoning in a "Strategic Notes" section before the brief.
```
Why it works: Forcing the GPT to articulate its reasoning before creating the brief results in more strategically sound recommendations.
Technique 2: Competitive Differentiation Framework
Add this analysis requirement:
```
For each competitor in the top 5 results, evaluate:
- Content depth: Superficial vs. comprehensive (score 1-5)
- Clarity: Confusing vs. clear explanations (score 1-5)
- Uniqueness: Generic vs. differentiated perspective (score 1-5)
- Actionability: Theoretical vs. practical guidance (score 1-5)
Our content must score higher in at least 3 of these 4 dimensions.
```
Result: Every brief includes a clear strategy for outperforming competitors, not just matching them.
Why scoring works: It forces qualitative assessment into quantitative comparison. Instead of "competitor has good examples," you get "competitor scores 4/5 on actionability because they include 3 step-by-step examples with screenshots, but lacks code samples." This specificity guides writers toward concrete improvements.
Competitive differentiation matrix in action:
This framework prevents the "me too" content trap. Your brief explicitly identifies where competitors are weak and how to exploit those gaps.
Technique 3: Structured Keyword Integration
Replace vague "use keywords naturally" with specific guidance:
```
Keyword Placement Requirements:
- Primary keyword: Exact match in title, first H2, first 100 words, URL slug
- Secondary keywords: One per H2 heading (don't force, but prioritize)
- LSI/related terms: Naturally integrated throughout body content
- Question keywords: Used as exact H2 or H3 headings where appropriate
For each heading suggestion, note which keyword variation it targets in [brackets].
Example: "How to Optimize Product Pages for SEO [secondary: product page seo]"
```
Benefit: Writers know exactly where to use which keywords without keyword stuffing.
Technique 4: Content Scope Control
Prevent overly broad or too narrow briefs:
```
Content Scope Guidelines:
- For short-tail keywords (1-2 words): Break into multiple focused pieces, don't try to cover everything
- For long-tail keywords (4+ words): Deep dive on the specific question, don't expand scope unnecessarily
- For commercial intent: Focus on comparison, features, pricing—minimize tangential information
- For informational intent: Provide comprehensive education, include examples and use cases
Adjust word count target based on scope. Signal to writer if topic warrants pillar content (3000+ words) vs. supporting cluster post (1500-2000 words).
```
Impact: Briefs correctly scope content, preventing sprawling posts that never get finished or too-thin posts that don't rank.
Integrating Custom GPTs Into Your Workflow
A great brief-generating GPT is useless if your team doesn't use it. Here's how to integrate it practically.
Integration 1: Content Calendar Planning
Monthly process:
1. Export keyword opportunities from your SEO tool (Ahrefs, SEMrush, etc.)
2. Upload CSV to your custom GPT
3. Request: "Generate briefs for all keywords in this file with search volume above [threshold] and keyword difficulty below [threshold]"
4. GPT outputs briefs for all qualified keywords
5. Review, prioritize, and assign to writers
Time savings: 30-40 hours of manual brief creation per month reduced to 2-3 hours of review.
Integration 2: Writer Assignment Process
Before assignment:
1. Generate brief with custom GPT
2. Add assignment-specific context (writer strengths, deadline, related content)
3. Export as markdown or PDF
4. Attach to task in project management tool (Asana, Monday, Notion)
Template for assignment:
```
Writer: [Name]
Due Date: [Date]
Word Count Target: [Range]
Priority Level: [High/Medium/Low]
[Full GPT-generated brief]
Additional Notes:
- [Any specific requirements for this piece]
- [Related content to reference]
- [Subject matter experts to interview if needed]
```
Integration 3: Content Refresh Workflow
Updating existing content requires different briefs than net-new creation.
Refresh brief prompt:
```
Generate a content refresh brief for this URL: [existing content URL]
Current performance:
- Organic traffic (last 30 days): [number]
- Average position: [number]
- Primary keyword: [keyword]
- Target keyword: [keyword we want to rank for]
Analyze the existing content and competitor landscape to determine:
1. What sections need expansion or updating
2. New subtopics to add based on current SERP
3. Outdated information to remove or update
4. SEO optimization opportunities (title, meta, headings, internal links)
5. Content gaps compared to competitors
Format as a brief highlighting what to CHANGE, not a full rewrite brief.
```
Why separate refresh prompts matter: Writers need different guidance for updates vs. new content. Refresh briefs focus on specific improvements, not full rewrites.
Integration 4: Batch Processing for Scale
When you need 50+ briefs at once:
Process:
1. Create spreadsheet with columns: Keyword, Search Intent, Target Audience, Content Type
2. Upload to custom GPT
3. Request: "Generate a brief for each row in this spreadsheet. Output as separate markdown files or a single document with clear separators."
4. GPT processes entire sheet
5. Export briefs, assign based on writer expertise and availability
Real client example: Generated 120 product page briefs in under 2 hours. Manual process would have taken 40+ hours. Quality was consistent enough that only 5% required significant revisions.
Technical Implementation: API Integration
For developers who want to automate brief generation programmatically:
OpenAI API Integration Example
// Node.js script to generate content briefs via OpenAI API
const OpenAI = require('openai');
const fs = require('fs');
const csv = require('csv-parser');
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY
});
// System prompt for content brief generation
const SYSTEM_PROMPT = `You are an expert SEO content strategist. Generate comprehensive content briefs following this structure:
- Strategic Context (keyword, intent, audience)
- SEO Requirements (title, meta, keywords)
- Content Structure (headings, word count)
- Research Foundation (competitors, gaps)
- Quality Criteria (takeaways, CTA)`;
async function generateBrief(keyword, searchIntent, targetAudience) {
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: [
{ role: "system", content: SYSTEM_PROMPT },
{ role: "user", content: `Generate a content brief for:
Keyword: ${keyword}
Search Intent: ${searchIntent}
Target Audience: ${targetAudience}` }
],
temperature: 0.7,
max_tokens: 2000
});
return response.choices[0].message.content;
}
// Process CSV of keywords
async function processBatchBriefs(csvPath) {
const briefs = [];
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.createReadStream(csvPath)
.pipe(csv())
.on('data', async (row) => {
try {
const brief = await generateBrief(
row.keyword,
row.search_intent,
row.target_audience
);
briefs.push({ keyword: row.keyword, brief });
console.log(`Generated brief for: ${row.keyword}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error processing ${row.keyword}:`, error);
}
})
.on('end', () => {
// Save all briefs to individual markdown files
briefs.forEach(({ keyword, brief }) => {
const filename = keyword.replace(/\s+/g, '-').toLowerCase();
fs.writeFileSync(`./briefs/${filename}.md`, brief);
});
resolve(briefs);
});
});
}
// Usage
processBatchBriefs('./keyword-list.csv')
.then(() => console.log('All briefs generated'))
.catch(error => console.error('Batch processing failed:', error));
Claude API Integration (Anthropic)
\# Python script using Claude API for content brief generation
import anthropic
import csv
import os
client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key=os.environ.get("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"))
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are an expert SEO content strategist. Generate comprehensive content briefs with:
1. Strategic Context (keyword intent analysis)
2. SEO Requirements (meta, title, keywords)
3. Content Structure (recommended headings)
4. Competitive Analysis (gaps to exploit)
5. Quality Criteria (key takeaways)"""
def generate_brief(keyword, search_intent, target_audience):
message = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=2000,
system=SYSTEM_PROMPT,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": f"""Generate a content brief for:
Keyword: {keyword}
Search Intent: {search_intent}
Target Audience: {target_audience}"""}
]
)
return message.content[0].text
def process_keyword_csv(csv_path):
briefs = []
with open(csv_path, 'r') as file:
reader = csv.DictReader(file)
for row in reader:
try:
brief = generate_brief(
row['keyword'],
row['search_intent'],
row['target_audience']
)
briefs.append({'keyword': row['keyword'], 'brief': brief})
print(f"Generated brief for: {row['keyword']}")
# Save to markdown file
filename = row['keyword'].replace(' ', '-').lower()
with open(f"./briefs/{filename}.md", 'w') as f:
f.write(brief)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {row['keyword']}: {e}")
return briefs
\# Run batch processing
if __name__ == "__main__":
briefs = process_keyword_csv('./keyword-list.csv')
print(f"Generated {len(briefs)} content briefs")
WordPress Integration: Auto-Create Draft Posts
<?php
// WordPress plugin code to create draft posts from GPT briefs
// Save as: wp-content/plugins/gpt-content-briefs/gpt-content-briefs.php
/*
Plugin Name: GPT Content Brief Importer
Description: Import AI-generated content briefs as WordPress draft posts
Version: 1.0
*/
function import_gpt_briefs_from_json($json_file_path) {
$briefs = json_decode(file_get_contents($json_file_path), true);
foreach ($briefs as $brief) {
// Parse the brief structure
$title = extract_title_from_brief($brief['content']);
$meta_description = extract_meta_from_brief($brief['content']);
$keywords = extract_keywords_from_brief($brief['content']);
// Create draft post
$post_data = array(
'post_title' => $title,
'post_content' => $brief['content'],
'post_status' => 'draft',
'post_author' => 1,
'post_type' => 'post',
'meta_input' => array(
'_yoast_wpseo_metadesc' => $meta_description,
'_yoast_wpseo_focuskw' => $keywords['primary'],
'content_brief_source' => 'gpt-generated'
)
);
$post_id = wp_insert_post($post_data);
if ($post_id) {
// Add custom fields for SEO data
update_post_meta($post_id, 'target_keywords', json_encode($keywords['secondary']));
update_post_meta($post_id, 'content_brief_date', current_time('mysql'));
echo "Created draft post: $title (ID: $post_id)\n";
}
}
}
function extract_title_from_brief($content) {
// Parse markdown to extract title tag recommendation
preg_match('/Title Tag.*?:\s*(.+?)(?:\n|$)/i', $content, $matches);
return $matches[1] ?? 'Untitled Post';
}
function extract_meta_from_brief($content) {
preg_match('/Meta Description.*?:\s*(.+?)(?:\n|$)/i', $content, $matches);
return $matches[1] ?? '';
}
function extract_keywords_from_brief($content) {
preg_match('/Primary Keyword.*?:\s*(.+?)(?:\n|$)/i', $content, $primary);
preg_match('/Secondary Keywords.*?:\s*(.+?)(?:\n|$)/i', $content, $secondary);
return [
'primary' => $primary[1] ?? '',
'secondary' => explode(',', $secondary[1] ?? '')
];
}
// Admin interface to trigger import
add_action('admin_menu', function() {
add_menu_page(
'GPT Brief Import',
'Content Briefs',
'manage_options',
'gpt-brief-import',
'render_import_page'
);
});
function render_import_page() {
if (isset($_POST['import_briefs'])) {
$upload_dir = wp_upload_dir();
$file_path = $upload_dir['path'] . '/briefs.json';
import_gpt_briefs_from_json($file_path);
}
echo '<div class="wrap">';
echo '<h1>Import GPT Content Briefs</h1>';
echo '<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">';
echo '<input type="file" name="briefs_json" accept=".json">';
echo '<input type="submit" name="import_briefs" value="Import Briefs" class="button button-primary">';
echo '</form>';
echo '</div>';
}
?>
Quality Control: Ensuring GPT-Generated Briefs Are Actually Useful
AI can generate nonsense confidently. Here's how to catch and fix issues before briefs reach writers.
The most dangerous AI output is the plausible-sounding error. A brief that looks comprehensive but recommends 800 words for a keyword that requires 3,000 to compete. A competitor analysis that cites outdated URLs. Keyword placement guidance that triggers over-optimization penalties.
Quality control isn't about perfection—it's about systematic verification of high-risk elements. Build your review process around failure modes, not best-case scenarios.
The Three-Stage Review Framework
Total review time: 8-15 minutes per brief vs. 60-90 minutes to create manually. Even with quality control, you're achieving 80%+ time savings.
Quality Checkpoint 1: SERP Accuracy Verification
Check: Do the top-ranking URLs in the brief actually rank for the target keyword?
Process:
- Open incognito window and search the primary keyword
- Compare actual top 5 results to what the brief lists
- Verify at least 3 of 5 URLs match current SERP
- If mismatched, regenerate with more specific instructions
Common failure modes:
Automated validation script:
// Check if competitor URLs in brief actually rank
async function validateCompetitorURLs(brief, keyword) {
const briefURLs = extractCompetitorURLs(brief);
const actualSERP = await fetchSERPResults(keyword);
const matches = briefURLs.filter(url =>
actualSERP.slice(0, 10).some(result =>
result.url.includes(url.domain)
)
);
const accuracy = (matches.length / briefURLs.length) * 100;
return {
accuracy,
valid: accuracy >= 60, // At least 3 of 5 should match
mismatches: briefURLs.filter(url => !matches.includes(url))
};
}
Red flag indicators:
- Competitor URLs are all from 2+ years ago
- Domains mentioned don't appear in top 20 SERP results
- Analysis references SERP features (PAA, Featured Snippets) not present in current results
- Word count recommendations deviate 40%+ from SERP median
Quality Checkpoint 2: Internal Linking Validation
Check: Do suggested internal links actually exist on your site? Process:
1. Review internal linking section of brief
2. Verify URLs are real (spot check 2-3)
3. Confirm links are contextually relevant to the new content
Fix for consistent errors: Add a regularly updated sitemap to the GPT's knowledge base with page titles and URLs.
Quality Checkpoint 3: Keyword Difficulty Reality Check
Check: Is the word count and content depth recommendation realistic for the keyword's competitiveness? Process:
1. Compare GPT's suggestions to your SEO tool's keyword difficulty score
2. For high-difficulty keywords (60+), ensure brief calls for pillar-length content (3000+ words)
3. For low-competition keywords, don't overkill—1500 words might be sufficient
Adjustment example: GPT suggests: 1800 words for "best project management software" Reality: This keyword has extremely high competition. Brief should call for 4000+ words, comparison table, video content, and expert quotes.
Quality Checkpoint 4: Search Intent Alignment
Check: Does the brief guide writers to match what searchers actually want? Process:
1. Review SERP for the keyword
2. Identify format patterns (listicles, how-tos, comparisons)
3. Ensure brief's structure recommendation matches dominant SERP format
Red flag: Brief suggests long-form guide when SERP is dominated by quick-answer lists. This signals intent misalignment.
Measuring Custom GPT ROI
How do you know if your custom GPT is actually improving content performance?
Most teams measure AI success by usage ("we use it for 80% of briefs!") rather than outcomes. Usage is vanity. Performance is value. Track metrics that connect to revenue and team efficiency.
The Complete ROI Dashboard
Speed Metrics: Time Is Money
Brief creation time breakdown:
Time to first draft: Faster briefs accelerate the entire content pipeline. When writers receive briefs immediately instead of waiting 3-5 days, they maintain creative momentum. Our clients see 40% reduction in draft completion time—not because writers work faster, but because they start sooner with better direction.
Revision cycles: This is where quality compounds. Each revision round costs 30-60 minutes of editor time plus writer revisions. Reducing from 2.5 to 1.5 rounds per post saves 30-60 minutes per piece. At 20 posts per month, that's 10-20 hours saved monthly.
Quality Metrics: Performance Per Post
Organic traffic comparison:
Why traffic increases: Better briefs lead to better content targeting, which matches search intent more accurately. GPT-briefed content ranks for more long-tail variations because the brief explicitly targets question keywords and semantic variations that manual briefs often miss.
Ranking position improvement:
Track first-page penetration rate:
- Pre-GPT: 42% of posts reach first page within 90 days
- Post-GPT: 58% of posts reach first page within 90 days
That 16-percentage-point improvement translates to 8 additional posts per 50-post content calendar achieving first-page visibility. If average first-page post generates 400 visits/month, that's 3,200 additional monthly visits from ranking improvement alone.
Scale Metrics: Volume Without Headcount
Content output trajectory:
Keyword coverage expansion:
Before GPT, SEO specialist created briefs for highest-priority keywords only (top 35% of opportunities). Lower-priority keywords went unaddressed because brief creation was the bottleneck.
With GPT, batch processing enables briefing for all viable keywords. Coverage jumps from 35% to 65%+ without additional headcount. This expanded coverage captures long-tail traffic that compounds over time.
Writer Satisfaction: Qualitative But Critical
Survey results from content teams using custom GPT:
Reduced back-and-forth:
Pre-GPT: Writers average 4.2 clarification questions per brief Post-GPT: Writers average 1.8 clarification questions per brief
That's 2.4 fewer interruptions per brief. At 20 briefs per month, that's 48 fewer slack messages, emails, or meeting requests—freeing up the SEO lead for strategic work.
Real Client Case Study: B2B SaaS Company
Context: Mid-market project management software company, 2-person content team, competing for high-difficulty keywords.
90-Day Results:
The unlock: They didn't add headcount. They didn't increase budget significantly. They systematized brief creation, which removed the bottleneck limiting content production. More content → more rankings → more traffic → more leads, all with minimal cost increase.
ROI was obvious within 60 days. By month 6, they had recouped the entire setup investment and were operating at 2.7x content output for 1.1x the cost.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
We've built dozens of custom GPTs for content programs. Here are the pitfalls to avoid.
Mistake 1: Treating GPT as a black box Problem: Team uses GPT without understanding what it's doing or why. Fix: Train your team on how the GPT works, what knowledge base documents it references, and how to spot low-quality outputs. Users should be critical consumers, not blind followers. Mistake 2: Not updating knowledge base Problem: GPT references outdated content inventory or stale competitive analysis. Fix: Set calendar reminder to update knowledge base documents quarterly. Add new high-performing content, remove outdated examples, refresh competitive intelligence. Mistake 3: One-size-fits-all briefs Problem: Using the same brief template for blog posts, landing pages, and product descriptions. Fix: Build multiple custom GPTs or add conditional logic to system prompt:
```
If content type is "product page":
- Focus on features, benefits, use cases
- Include comparison to alternatives
- Shorter word count (800-1200)
- Strong conversion focus
If content type is "blog post":
- Educational angle
- Comprehensive coverage
- Longer word count (1500-2500)
- Lead generation focus
```
Mistake 4: Skipping the refinement phase Problem: Using GPT outputs as-is without validation or editing. Fix: Always review GPT briefs before sending to writers. Look for hallucinated data, misaligned strategy, and generic recommendations. 10 minutes of review prevents hours of wasted writing effort.
Your Implementation Plan
Building a custom GPT for content briefs isn't a weekend project—plan for 2-4 weeks of setup and refinement.
This phased approach prevents the "big bang" rollout that overwhelms your team and produces unusable output. You're encoding months of content strategy expertise into a tool. That requires iteration, testing, and refinement.
Implementation Timeline and Milestones
Week 1: Foundation
Goal: Establish the structural foundation and initial AI configuration.
Day 1-2: Define brief requirements
Create your brief template document. Don't start from scratch—analyze your 10 best-performing pieces of content and reverse-engineer what made their briefs effective.
Evaluation framework:
For each high-performing post, document:
□ What sections were included in the brief
□ How specific was the keyword guidance
□ What competitor analysis was provided
□ What differentiation strategy was specified
□ How detailed was the structure recommendation
□ What quality criteria were set
Common patterns = your template requirements
Day 3-4: Gather knowledge base documents
Day 5: Write system prompt v1
Start with the template provided in this guide. Customize these sections:
- Brand voice guidelines (replace with your actual tone descriptors)
- Content standards (your specific quality requirements)
- Industry context (terminology, audience specifics)
- Validation checklist (your non-negotiable elements)
Day 6-7: Configure custom GPT
Create the GPT in ChatGPT with:
- System prompt installed
- Knowledge base uploaded
- Web browsing enabled
- Conversation starters configured
- Test with 3 keywords to verify basic functionality
Week 2: Testing & Refinement
Goal: Identify failure modes and refine prompts to achieve 70%+ usability.
Testing matrix:
Day 8-10: Generate 15 test briefs
Use the matrix above. For each brief:
- Generate without modifications
- Review against your quality checklist
- Document specific issues found
- Rate usability 1-10
Common issues discovered during testing:
Day 11-14: Iterative refinement
For each identified issue:
- Update system prompt with specific constraint
- Regenerate the briefs that failed
- Verify the fix worked
- Test on new keywords to ensure no regression
Document each change in a "Prompt Evolution Log" so you can track what improvements worked.
Refinement checklist before moving to pilot:
□ Briefs consistently include all 5 required sections
□ Keyword placement guidance is specific (not "use naturally")
□ Competitor analysis includes specific gaps and scores
□ Word count targets reference SERP data
□ Internal linking suggestions are real URLs
□ Brand voice matches your guidelines
□ At least 70% of test briefs rated 7+/10 usable
Week 3: Pilot with Real Content
Goal: Validate GPT briefs drive quality content in production environment.
Day 15-17: Select pilot content
Choose 10 keywords for pilot:
- 3 high-priority (important to get right)
- 4 medium-priority (typical workload)
- 3 low-priority (acceptable if imperfect)
This mix prevents risking critical content while providing realistic testing scenarios.
Day 18-19: Generate and review pilot briefs
For each keyword:
- Generate brief with custom GPT
- Review with quality control checklist (10 min max)
- Make minor adjustments if needed
- Send to writer with feedback form
Writer feedback form:
For each brief, please rate 1-10:
□ Clarity of strategic context
□ Specificity of SEO requirements
□ Usefulness of structure recommendations
□ Value of competitor analysis
□ Confidence this brief will lead to high-quality content
What was most helpful?
What was missing or unclear?
How does this compare to previous briefs you've received?
Day 20-21: Content production
Writers create first drafts. Track:
- Time to complete draft
- Questions asked during writing
- Issues encountered
Results analysis framework:
Week 4: Full Rollout
Goal: Achieve 100% team adoption with documented processes.
Day 22-23: Team training session
Training agenda (90 minutes):
- Why we built this (10 min) - Business case, efficiency gains expected
- How it works (15 min) - Demo of generating briefs, uploading keyword lists
- Quality control (20 min) - Review checklist, common failures, how to spot issues
- Hands-on practice (30 min) - Each person generates 2 briefs, reviews with group
- Integration into workflow (15 min) - When to use, how to request, where to save
Training materials to prepare:
- Video walkthrough (10 min screencast)
- Quality control checklist (1-page PDF)
- Troubleshooting guide (common issues and fixes)
- Prompt refinement protocol (how to suggest improvements)
Day 24-25: Process documentation
Create these documents:
- Brief Generation SOP: Step-by-step process from keyword to published brief
- Quality Control Guide: Validation checklist and review process
- Troubleshooting Playbook: Common issues and solutions
- Continuous Improvement Protocol: How to suggest prompt updates
Day 26-28: Integration and monitoring
Content calendar integration:
Old process:
Keyword research → Wait for brief (3-5 days) → Assign to writer → Draft → Edit → Publish
New process:
Keyword research → Generate briefs (same day) → Review → Assign to writer → Draft → Edit → Publish
Time saved: 3-5 days per piece
Monitoring dashboard:
Track these metrics weekly for first month:
- Briefs generated
- Average review time
- Writer satisfaction scores
- Briefs requiring major revision
- Content published from GPT briefs
- Performance metrics (traffic, rankings)
After 30 Days: Optimization & Scaling
Measurement review:
Compare pre/post metrics:
□ Brief creation time reduced 70%+
□ Content output increased 50%+
□ Writer satisfaction improved 30%+
□ Quality maintained or improved
□ ROI positive within 60 days
Continuous improvement cycle:
Monthly review process:
- Analyze brief quality scores - Identify patterns in low-rated briefs
- Review content performance - Do GPT-briefed posts rank/convert well?
- Gather team feedback - What's working? What's frustrating?
- Update system prompt - Refine based on learnings
- Test updates - Generate 5 new briefs, verify improvements
- Document changes - Track prompt evolution
Scaling considerations:
Once your primary brief GPT is working well:
- Build specialized GPTs for different content types (product pages, comparison posts, technical docs)
- Create batch processing workflows for content calendar planning
- Develop API integrations for automated brief generation
- Train GPT on new content types as your strategy evolves
The investment pays for itself quickly—most teams see ROI within the first month. By month 3, it's an indispensable part of your content operations.
--- Ready to scale your content program with AI? WE•DO builds custom GPT solutions for content teams at WordPress and Shopify brands. We handle the technical setup, prompt engineering, and team training—you get more content, faster, without sacrificing quality. Let's discuss your content challenges. Related reading:
- The Complete Guide to AI-Accelerated SEO for Shopify & WordPress (Pillar post)
- How to Use Claude/ChatGPT for Keyword Research in 10 Minutes
- AI vs. Human: Where to Draw the Line in SEO Content
Ready to Transform Your Growth Strategy?
Let's discuss how AI-powered marketing can accelerate your results.




